一、驱动程序分类
字符设备驱动:软件操作设备是是以字节为单位进行。
块设备驱动:EMMC、SD卡、Flash、U盘。
网络设备驱动:有/无线网络。
一个设备可属于多种设备类型: USB WiFi设备 => 字符设备 + 网络设备。
二、驱动架构
应用程序在用户空间,驱动程序在内核空间,运行在内核态。
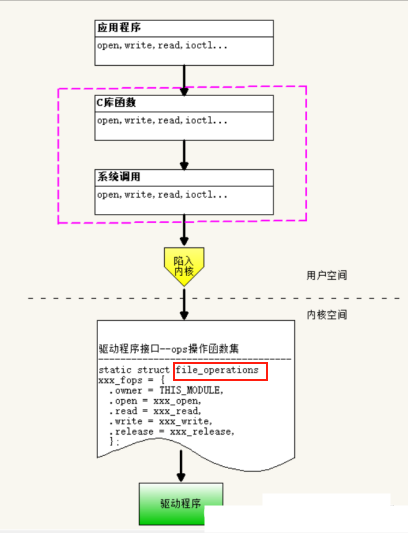
1. 驱动程序功能:
- 系统调用:内核 <–> 应用程序
- 驱动程序:内核 <–> 硬件设备
- 初始化和释放硬件设备
- 读/写设备信息
- 处理设备错误
2. 驱动代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
static int __init xxx_init(void) { //驱动入口函数
// 注册设备,申请设备
return 0; // 返回设备号
}
static void __exit xxx_exit(void) { //驱动出口函数
// 注销设备、设备号、类
}
module_init(xxx_init); //注册入口函数
module_exit(xxx_exit); //注册出口函数
3. 驱动程序编写流程
- 确定主设备号,也可以让内核自动分配;
- 定义自己的
file_operations结构体 - 实现对应的
drv_open/drv_read/drv_write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 - 把
file_operations结构体告诉内核register_chrdev - 编写入口函数,安装驱动程序时,就会去调用这个入口函数
- 编写出口函数,卸载驱动程序时,出口函数调用
unregister_chrdev - 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点
class_create,device_create
4. 框架代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
static int major = 0; // 确定主设备号
static char kernel_buf[1024];
static struct class *xxx_class;
#define MIN(a, b) (a < b ? a : b)
/*
* @description : 从设备读取数据
* @param - file : 内核中的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要存储读取的数据缓冲区(就是用户空间的内存地址)
* @param - size : 要读取的长度
* @param - offset : 相对于文件首地址的偏移量(一般读取信息后,指针都会偏移读取信息的长度)
* @return : 返回读取的字节数,如果读取失败则返回-1
*/
static ssize_t xxx_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {
int err;
// 驱动程序要打印信息使用printk
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
// 驱动程序传数据到用户空间copy_to_usr
err = copy_to_user(buf, kernel_buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - file : 内核中的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备驱动的数据缓冲区
* @param - size : 要写入的长度
* @param - offset : 相对于文件首地址的偏移量
* @return : 返回写入的字节数,如果写入失败则返回-1
*/
static ssize_t xxx_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
// 用户空间传数据给驱动(设备)
err = copy_from_user(kernel_buf, buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - node : 设备节点
* @param - file : 文件描述符
* @return : 打开成功返回0,失败返回-1
*/
static int xxx_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 关闭设备
* @param - node : 设备节点
* @param - file : 文件描述符
* @return : 关闭成功返回0,失败返回-1
*/
static int xxx_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations xxx_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = xxx_drv_open,
.read = xxx_drv_read,
.write = xxx_drv_write,
.release = xxx_drv_close,
};
static int __init xxx_init(void) {
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
// 向内核注册结构体
major = register_chrdev(0, "xxx", &xxx_drv);
// 自动创建设备节点
xxx_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "xxx_class");
err = PTR_ERR(xxx_class);
if (IS_ERR(xxx_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "xxx");
return -1;
}
device_create(xxx_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "xxx");
return 0;
}
static void __exit xxx_exit(void) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(xxx_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(xxx_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "xxx");
}
// 指定驱动的入口和出口,以及声明自己的驱动遵循GPL协议,不声明的话无法把驱动加载进内核
module_init(xxx_init);
module_exit(xxx_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
三、LED示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.read = led_read,
.write = led_write,
.release = led_release,
};
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - filp : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 从设备读取数据
* @param - filp : 要打开的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @param - buf : 返回给用户空间的数据缓冲区
* @param - cnt : 要读取的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 读取的字节数,如果为负值,表示读取失败
*/
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) {
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) {
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[1];
unsigned char ledstat;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
printk("kernel write failed!\r\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
ledstat = databuf[0]; // 获取状态值
if(ledstat == LEDON) {
led_switch(LEDON);
} else if(ledstat == LEDOFF) {
led_switch(LEDOFF);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 关闭/释放设备
* @param - filp : 要关闭的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int led_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
return 0;
}
static int __init led_init(void) {
int retvalue = 0;
u32 val = 0;
/* 初始化LED */
/* 1、寄存器地址映射 */
IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(CCM_CCGR1_BASE, 4);
SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE, 4);
SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE, 4);
GPIO1_DR = ioremap(GPIO1_DR_BASE, 4);
GPIO1_GDIR = ioremap(GPIO1_GDIR_BASE, 4);
/* 2、使能GPIO1时钟 */
val = readl(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
val &= ~(3 << 26); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (3 << 26); /* 设置新值 */
writel(val, IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
// 3、设置GPIO1_IO03的复用功能,将其复用GPIO1_IO03,最后设置IO属性
writel(5, SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
/*寄存器SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03设置IO属性
*bit 16:0 HYS关闭
*bit [15:14]: 00 默认下拉
*bit [13]: 0 kepper功能
*bit [12]: 1 pull/keeper使能
*bit [11]: 0 关闭开路输出
*bit [7:6]: 10 速度100Mhz
*bit [5:3]: 110 R0/6驱动能力
*bit [0]: 0 低转换率
*/
writel(0x10B0, SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
/* 4、设置GPIO1_IO03为输出功能 */
val = readl(GPIO1_GDIR);
val &= ~(1 << 3); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (1 << 3); /* 设置为输出 */
writel(val, GPIO1_GDIR);
/* 5、默认关闭LED */
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val |= (1 << 3);
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
/* 6、注册字符设备驱动 */
retvalue = register_chrdev(LED_MAJOR, LED_NAME, &led_fops);
if(retvalue < 0) {
printk("register chrdev failed!\r\n");
return -EIO;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_exit(void) {
/* 取消映射 */
iounmap(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
iounmap(SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(GPIO1_DR);
iounmap(GPIO1_GDIR);
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
unregister_chrdev(LED_MAJOR, LED_NAME);
}